Scalability
If you find configuring scalability overwhelming, consider using Colyseus Cloud to easily deploy and scale your Colyseus servers.
You do not need to specify driver, presence, or publicAddress when using Colyseus Cloud.
How does Colyseus achieve scalability?
- Increasing the number of processes will increase the amount of rooms that can be created.
- Rooms are equally distributed across the available processes.
- Each Room belongs to a single Colyseus process.
- Each process has a maximum amount of players it can handle. (The exact amount depends on many factors. See our FAQ.)
- Client connections are directly associated with the process that created the room.
Redis is required for scaling.
Check out the diagram of how matchmaking works with scaling infrastructure and multiple processes.
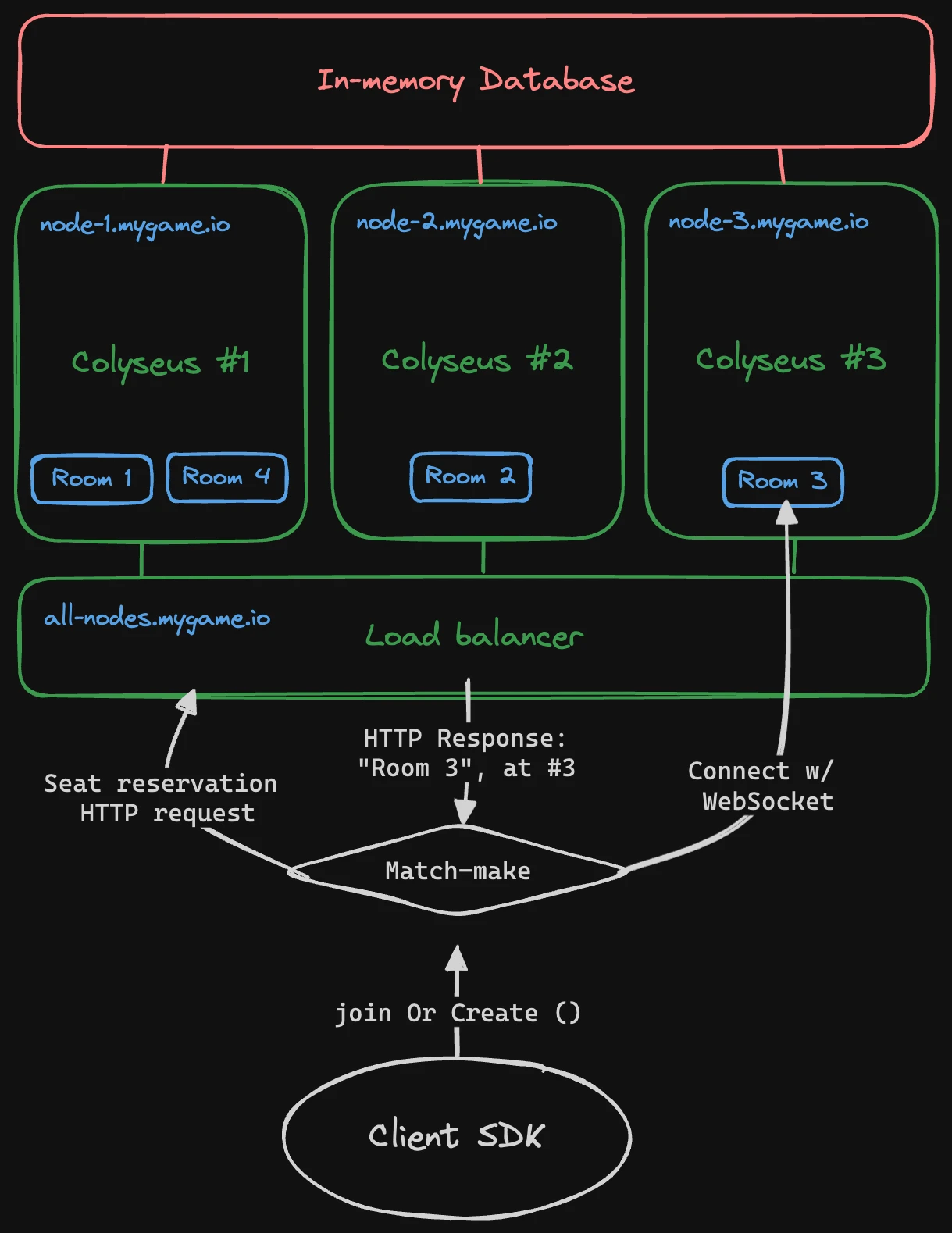
Use a shared Presence and Driver
import { defineServer } from "colyseus";
import { RedisPresence } from "@colyseus/redis-presence";
import { RedisDriver } from "@colyseus/redis-driver";
const server = defineServer({
// ...
presence: new RedisPresence(),
driver: new RedisDriver(),
});The process to join a Room consists of two requests:
- Reserve a seat in the Room: Any of the Colyseus processes can handle this request. By using a shared
presenceanddriver, the framework is able to communicate internally via pub/sub to reserve a seat, or create a new room if necessary. - Establish a WebSocket connection with the Room: The client will use the seat reservation information to connect directly to the process that created the room.
See Presence API and Driver.
Make each Colyseus process publicly accessible
Configure each Colyseus process to use its very own public address, so clients can connect directly to it.
import { defineServer } from "colyseus";
// ...
const server = defineServer({
driver: new RedisDriver(),
presence: new RedisPresence(),
// use a unique public address for each process
publicAddress: `backend.yourdomain.com/${(Number(process.env.PORT) + Number(process.env.NODE_APP_INSTANCE))}`,
// ...
});You may have a regular load balancer sitting behind all the Colyseus processes in order to distribute the incoming connections. The load balancer must be the initial entrypoint.
Spawn multiple Colyseus processes
To run multiple Colyseus instances in the same server, you need each one of them to listen on a different port number. It’s recommended to use ports 2567, 2568, 2569, 2570, and so on.
The PM2 Process Manager is recommended for managing multiple Node.js app instances, but not required.
npm install -g pm2Use the following ecosystem.config.js configuration:
const os = require('os');
module.exports = {
apps: [{
port : 2567,
name : "colyseus",
script : "lib/index.js", // your entrypoint file
watch : false,
instances : os.cpus().length, // or manually set the amount of instances
exec_mode : 'fork', // IMPORTANT: DO NOT use 'cluster' mode.
}]
}When you use @colyseus/tools’s .listen() method, the NODE_APP_INSTANCE from PM2 is automatically used to define the port number. If you specified 2567 as port number, the first instance will listen on port 2567, the second instance on port 2568, and so on.
Now you’re ready to start multiple Colyseus proceses.
pm2 start ecosystem.config.jsTypeScript Users - It is recommended compile your TypeScript files before running pm2 start, via npx tsc. Alternatively, you can install the TypeScript interpreter for PM2 (pm2 install typescript) and set the exec_interpreter: "ts-node".
Use NGINX as a reverse proxy
Install nginx and configure it to proxy requests to your Colyseus processes.
The following NGINX config file will:
- Proxy requests to
backend.yourgame.comto the Colyseus processes running on ports2567,2568,2569,2570, and so on. - Dynamically use the port number from the URL, e.g.
backend.yourgame.com/2567/will proxy to the Colyseus process running on port2567.
error_page 502 /error.html;
upstream colyseus_servers {
server 127.0.0.1:2567;
server 127.0.0.1:2568;
server 127.0.0.1:2569;
server 127.0.0.1:2570;
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name backend.yourgame.com;
ssl_certificate /root/certs/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /root/certs/privkey.pem;
# Proxy to the colyseus_servers upstream
location / {
proxy_pass http://colyseus_servers/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
proxy_read_timeout 86400s;
proxy_send_timeout 86400s;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_502;
include proxy_params;
}
# Dynamically use the port number from the URL
location ~ "^/(?<PORT>2[0-9]{3})/(.*)" {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:$PORT;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
proxy_read_timeout 86400s;
proxy_send_timeout 86400s;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_502;
include proxy_params;
}
location /error.html {
root /var/www/html;
internal;
}
}Use Let’s Encrypt or ZeroSSL to get SSL certificates
It is recommended to use SSL certificates to secure the communication between the client and the server. Replace the ssl_certificate and ssl_certificate_key paths in the NGINX configuration file with your own SSL certificates.